Background: The treatment of relapsed/refractory AML (r/r AML) patients are still an unmet medical need in clinic. In recent years, cellular immunotherapy especially CAR-T cell therapy played more important roles in hematological malignancies. Unfortunately, the safety and efficacy of existing cell therapies to r/r AML patients still facing many challenges and needs to be further improved. Our previous studies have demonstrated that Double Negative T cells (DNTs) showed strong cytotoxicity to AML blasts and can improve the prognosis of AML patients relapsed after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Here, we reported our ongoing phase I clinical trial of RC1012 injection (allogeneic DNT cells) in patients with r/r AML (NCT05471323). This study protocol was approved by Chinese NMPA (National Medical Products Administration). Informed consent was obtained in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Objective: Explore the efficacy indicator in r/r AML patients after allogeneic DNT cells therapy.
Methods: 7 patients with r/r AML were enrolled in the trial according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. DNTs from peripheral blood of healthy donors were manufactured in GMP facility. After lymphodepleting chemotherapy with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, each patient received three infusions of HLA-mismatched DNT cells at 1.5×10^8 cells/kg with one week interval. The PK data were collected and analyses as well as the checkpoint inhibitors on T cells was monitored.
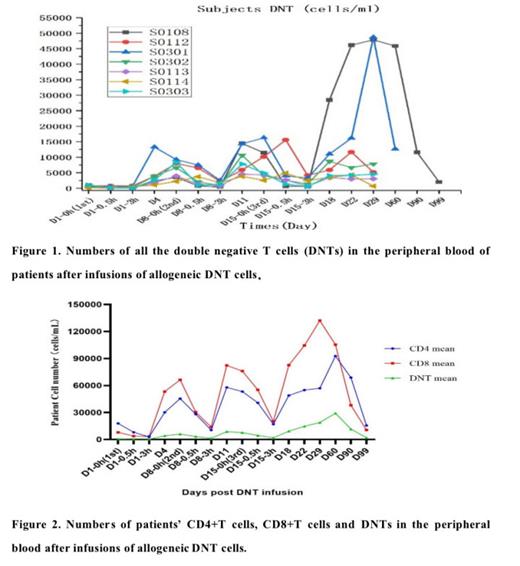
Results: As reported before, DNT cells had shown good safety profile in the treatment of r/r AML. Multiple infusions of allogeneic DNT cells can benefit some patients with r/r AML. Allogeneic DNT cell therapy can stimulate the patient's DNT cells to proliferate, and the DNT cells level in peripheral blood corelated to the disease outcomes. Allogeneic DNT cells can also stimulate the patient's CD4 and CD8 cells to proliferate and is favorite the CD8 cells to grow, indicating its potential to enhance the anti-tumor activities after DNT cells therapy. Allogeneic DNT cells have no toxicity to normal bone marrow cells, and the quick recovery of platelet counts in peripheral blood corelated to the efficacy of the DNT cells therapy. TIGIT, PD-1, CD57 are increased on patients' T cells which may hinder the effect of immunotherapy in r/r AML patients.
Conclusions: Allogeneic DNTs therapy are safe in clinical treatment and can reduce tumor burden after infusion with the increase of patient's DNT cells in complete remission and partial remission patients. These findings warrant the allogeneic DNTs as a novel adjuvant therapy with allo-HSCT to enhance the treatment efficacy in r/r AML. The finding of TIGIT, PD-1, CD57 molecules were increased on patients' T cells indicated that the combination of DNTs with immune checkpoint inhibitors may further improve the DNTs efficacy in r/r AML patients.
Key words: Double negative T cells (DNTs), AML, Immunotherapy
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal